厚生労働省所管
The Polytechnic University of Japan Official Web Site
The Polytechnic University of Japan Official Web Site
1. History of PTU Japan
| 1961 | Establishment of the Tokyo Vocational Training Center at Kodaira city of Tokyo Long term training school : 8 departments with 80 students Dept. of forging and casting, mechanics, sheet metal and welding, electrics 1, electrics 2, mechanics of transportation, wood machining, painting |
|---|---|
| 1965 | Establishment of PTU Central Vocational Training Center was reorganized to PTU and attached Central Vocational Training Center |
| 1973 | Movement of PTU to Sagamihara City, Kanagawa Prefecture and began to educate VET instructors thru its undergraduate course |
| 1978 | Establishment of Vocational Training Research center |
| 1988 | Establishment of Master Course of Engineering |
| 2011 | Polytechnic University of Japan was organized under the incorporated administrative agency "the Japan Organization for Employment of the Elderly, Persons with Disabilities and Job Seekers" and the Polytechnic University decided to close its undergraduate and graduate courses. Its main role became
|
| 2012 | Established new undergraduate course of "Bachelor of Science in Manufacturing Technology" |
| 2013 | Integrated campus to Tokyo and closed its Sagamihara campus |
| 2014 | Started long term and short term course for VET instructors |
| 2015 | The Institute of Research and Development moved and was integrated into Kodaira Campus |
| 2016 | Established graduate course of "Master of Science in Manufacturing Engineering! |
Beginning term for modernization of manufacturing technology , and PTU provided more useful VET instructors to national/public/private polytechnic colleges and centers in Japan
Developing term for higher products manufacturing, and PTU began to provide more VET instructors.
New term for a new economical period of Japan , and PTU must review its work and began to revise them.
2. PTU Organization
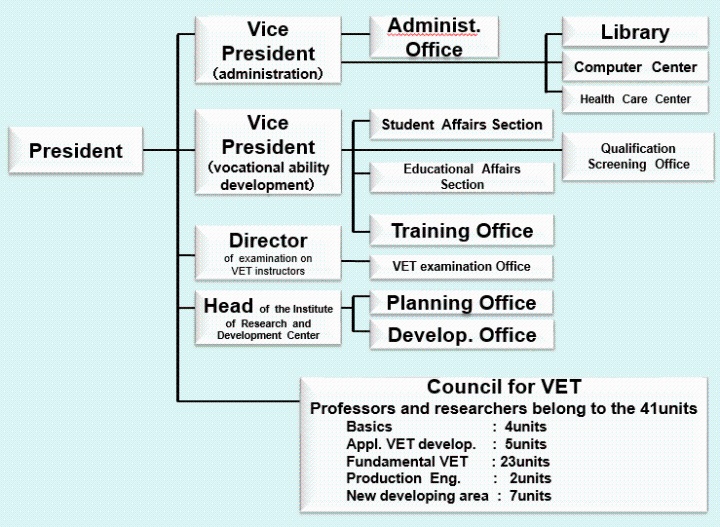
3. Four Functions and Roles of PTU
1. Training of VET instructors
Long-term training course and Short-term training course
- To train in additional abilities including advanced expertise and skills and instruction techniques necessary to become high-level VET instructors; in order to receive such training, people must be employees of JEED, the prefectural governments, companies, etc. hired to be VET instructors and meet requirements such as some experience in the private sector and degrees from engineering universities.
Training subject- change course
- To train VET instructors, etc. to obtain VET instructor licenses in new or additional subjects.
Advanced training course
- To train VET instructors to teach advanced subjects in applied courses at PTU
2. Re-training of VET instructors
Training courses
- To re-train the current VET instructors in:
1. Advanced technologies and expanded specialties to respond to technological innovations, etc.; and
2. Instruction techniques, development of training materials, etc. to upgrade their instruction abilities - Some courses are provided in regional areas ("catered training") to improve conditions of participation
- The scope of eligible participants is expanded to include those holding leading positions in private educational and training institutions, to provide need-based training, in such areas as instruction techniques.
※Results in FY2017
Number of courses: 551; number of
students: 5,831
Breakdown:
VET instructors in prefectural
governments: 1,783
VET instructors in JEED: 2,417
Others: 1,631
3. Survey & research
Survey & research
- Conduct survey & research necessary to make VET instruction practical and keep it up to date to the changes in industrial structures, technologies, etc.
Development of training materials, courses, etc.
- Develop current and near-future training materials that contribute to implementation of effective VET
Development of training techniques, evaluation methods, etc.
- Disseminate information on training outcomes, etc.: e.g. TETRAS
4. Bachelor course
Undergraduate course in Bachelor of Science in Manufacturing Technology
- The course aims to train "process innovators" who have knowledge of science, technology as well as skill and are active in the future at the Monodzukuri sites. Bachelor's degrees are offered by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Science and Technology. A selected few group -- 80 students per grade -- studies Mechanical Engineering, Electrical Engineering, Electronics Information, or Architectural engineering.
- The number of credit hours for completing the requirements is 5,600 hours/four years -- nearly twice as those required in general colleges in Japan of which about 3,300 hours (60%) are devoted to practice and experiments.

4. Education of new VET instructors
4-1. Outline of VET
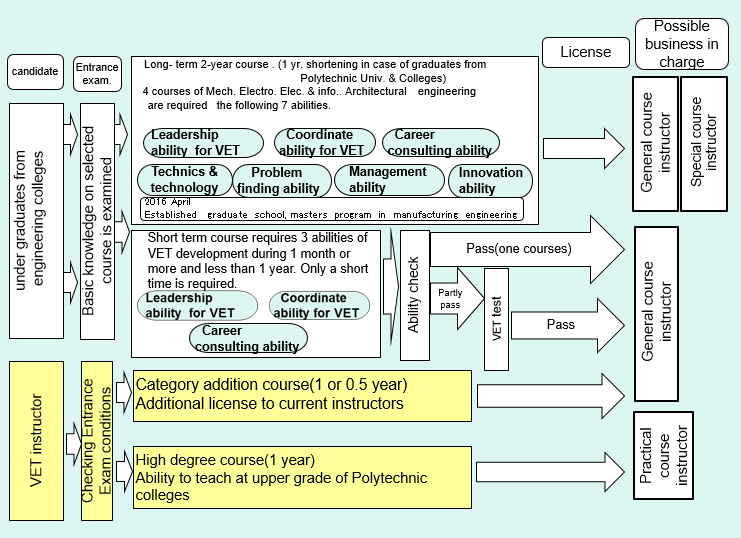
4-2. Outline of long term education system for VET instructors
1. Candidate
Those who have passed entrance exam. for VET candidates or those who wish to be VET instructors, and to satisfy any of the following conditions.
- Graduated from the department of colleges which are admitted by Japanese School Education Act and related to the desired license field.
- Graduated from 4-year polytechnic colleges.
- Those who possess the similar level of knowledge as the above 1 or 2
2. Aims of education
After the current course, the graduates must possess capability to work at VET schools and centers as 3-year experienced instructors. They must manage to decide local VET policy, practical ability to work at VET, to support students to get a job (career consulting ability, formation of job cards, finding new business, etc.) as well as an evaluation of VET contents and its improvement.
3. Characteristics of Curricula
- To gain technical level equivalent to Trade Skill Test 1.
- To gain knowledge and practice to fit to career consultant.
- To strengthen practical power to meet for increase of vocational training subjects (1080 hours).
- To adapt for modern industrial and technological trend of advanced subjects.
- To strengthen higher level of shop safety potentials by gaining life support knowledge as AED and emergency in addition to conventional safety and security subjects.
- To admit VET instructor license to graduates of long- term course (mechanical, electrical, electro-information, architectural engineering)
4. Ability to gain
Leadership ability for VET
To train trainers from the young to the aged to the level of specified VET level under a given time and training environment by possessing abilities of VET.
To manage VET training based on the PDCA cycle.
Coordinate ability for VET
To set a new course and/or review old ones according to requirements of enterprises and workers.
To advise and propose a VET plan of companies hearing their needs.
Career consulting ability
To consult career similar with those who finished a140- hour career consultant model proposed by the Ministry of Health,Labour and Welfare.
Technics & technology
To assist upgrading QCDSE(Quality, Cost, Delivery, Safety and Environment) at shop thru. manufacturing technics and technology of manufacturing, assembly and inspection of parts.
Problem finding ability
To find substance of facing problems and to analyze their merit /demerit and to improve the problem.
Management ability
To support proper technique and technology to realize high reliability, low cost, short delivery time on production line.
Innovation ability
To support the proposal of plan to innovate actions from manufacturing site,understanding company's strategy
4-3 Ability to be gained by learning subjects of long- term 2-year course.
-Case of Mechanical Education Course-
Technic/Technology, Innovation ability, Management ability, Problem finding ability, Career consulting ability, Coordinate ability for training, Leadership ability for VET
Special subject
-mechanical control
hydraulics / aeronautics / production eng.
-mechanical design and manufacturing
manufacturing
measurement
NC
-management
process manage.
quality control
factory manage..
product develop.
and management
-energy engineering
energy engineering
Special exercise
-exercise on automatic control
mechatronics 1,2
sequence control
-exercise on mechanical control
Hydraulics / aeronautics
-exercise on mechanical drawing and machining
machining
machine tools
NC machine tools
CAD/CAM exercise
technic exercise
precision machining
-safety and clean operation
safety and clean
operation
-applied exercise of mechanical training
applied training exercise
applied exercise of precision machining
assembly of precise mechanics
assembly of automatic machines
Common subject
-outline of advanced technology
bio-engineering
injection & licensing
-safety/security control
safety/security guidance
Ability development exercise
-practice of subject teaching
teaching method for each special subject
supporting system for learners
training practice
-practice of VET management
improve training practice
coordination practice 1,2,3
-exercise career support systems
career technics 1 and 2
career consulting for VET゙
exercise career consulting
exercise employment
group approaching
human relation networking
Ability development subject
-psychology of VET
psychology for VET
-principle of vocational training
principle of VT
related law of VT
-supporting career formation
counseling & career consulting
Counseling technology
-teaching method
lecture planning
development of teaching materials
supporting method for learners
-teaching & training management
assessment of training
development & operation of course outside training
supporting method
human resource supporting systems

Educating high level of VET instructors who possess such 7 practical training abilities as to teach and train workers
curriculum of long- term education system for VET instructors
| Training course | 1. Common | 2. Vocational development | 3. Vocational development practice | 4. Course subject | 5. Course practice | total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanical training course | 108hours | 432hours | 1,260 hours * | 396hours | 1,404hours | 3,600hours |
| Electricaltraining Course | 108hours | 432hours | 1,260 hours * | 468hours | 1,332hours | 3,600hours |
| Electronic info. training course | 108hours | 432hours | 1,260hours * | 432hours | 1,368hours | 3,600hours |
| Architectural training course | 108hours | 432hours | 1,260hours * | 468hours | 1,332hours | 3,600hours |
* 1,080 hours is occupied by practice at training place
4-4 Graduate Course of Master of Science in Manufacturing Engineering” (Master’s course)
1. Qualification for receiving the course
Those who have passed entrance examination for VET candidates or those who wish to be VET instructors, and to satisfy any of the following conditions.
- Graduated from 4 year polytechnic colleges of faculty of manufacturing science and technology or practical course.
- Graduated from the department of colleges which are admitted by Japanese School Education Act and related to the desired license field.
- Those who possess the similar level of knowledge as the above 1 or 2.
2. Outline of Graduate Course of Master of Science in Manufacturing Engineering.
| Aim | To train leaders in the field of human resources development who have up-to-date knowledge, technologies and skills and be able to develop VET instruction techniques etc. with research thinking. |
|---|---|
| Major | Department of Mechanical Engineering / Electrical Engineering / Electronics and Informatics / Architecture |
| Quota | 20 (about 5 for each department) |
| Term | 2 years *we do not shorten the training them for those who completed faculty of manufacturing science and technology or practical course. |
| Master's degree | Master of Science in Manufacturing Engineering |
3. Curriculum structure
2 years
- Special subject / exercise
- Ability development subject / exercise
- Advanced course (lecture subject)
- Research paper (special experiment exercise)

Special and Ability development subject/exercise (including facilities practice)
- Learn skills required for VET instructor
- Acquire VET instructor license
Advanced course and Research paper
- Learn advanced skills required for VET instructor
- Acquire degree (Master of Science in Manufacturing Engineering)
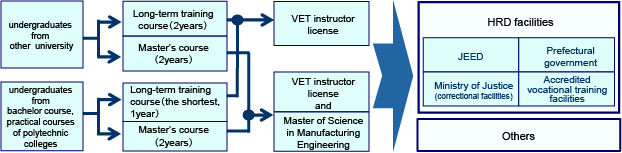
4-5 Place of employment after completion
4-6 Ability to be gained by learning subjects of short term course
1. Students
The following one of 5 who are employed or wish to work as VET instructor.
- those who are permitted to try VET instructor exam. by Japanese VET law 30-3.
- those who are permitted to receive seminars VET law of enforcement regulation 39-1
by the Ministry of Health, Labour and welfare - those who wish to become VET instructor
- those who are working as VET instructor
- those who received VET instructor exam. By VET law 28-1.
2. Training hour, subject
Necessary subjects can be selected among those of long- term training course in accordance with its training program.
Subjects are, Working ability for VET, Coordinate ability for VET, and Career consulting ability.
Leadership ability for VET(144hours)
Subject relating to VET instructor
- Course design (36H)
- Material development (36H)
- Supporting method students (36H)
- Teaching method of technics (36H)
Coordinate ability for VET(144hours)
Subject relating to coordinate ability
- Course development and management (36H)
- Training support method outside of training place (36H)
- Human resource development (36H)
- Coordination exercise (36H)
Career consulting ability(144hours)
Subject relating to Career condulting
- Outline of career consulting (36H)
- Theory of career consulting (36H)
- Basic skill for career consulting (36H)
- Practice of career consulting (36H)
3. Course feature
- To provide only insufficient subject and ability to those who possess various experience
- Those pass the ability check who are admitted as those who graduated from long- term course.
4-7 Outline of VET instructors' entering into new vocational categories
- aim
6 months or 1 year training course to give a new or additional VET instructor license - department(following 15 kinds )
mechanical engineering, structural iron works, plastics, welding, electrics, electrical operations, electronics, computer controls, architecture, wood works, plumbing, mechatronics, information control, painting, designing
4-8 outline of VET instructors' advanced training course
- aim
1 year course to give special and applicable ability as well as research ability to those who graduate from PTU graduate course or admitted under similar circumstances.
The graduates can teach at practical courses of polytechnic colleges.
5. Re-training of current VET instructors
Course of expanding specialty, updating training potentials, and introducing business to graduates, etc. . 551 classes, 5831 VET instructors inFY2017.
training course
Training new instructors courses (5 Days):teach fundamental knowledge and technics.
Training general instructors (2~5Days) courses:teach various kinds of knowledge and skills outside of special knowledge, technics and technology.
Training particular subjectcourses(5days to 1 yr) :teach contentsindepth at the dispatched companies.
Training method developmentcourses(2~10 Days) :teach efficient training methods, training materials, and design of training course based on needs.
Training practical technic and technology(2~5 Days) :teach skill improvement of specialty and curriculum, workshop planning and management.
RevisionofcurriculaduetochangesofneedsinVETetc, and new curricula development

Ability to teach technics of wooden buildings for VET instructors

6. Survey, Research and Development (InstituteofR & DCenter)
Survey & research on necessary VET instruction
- JobDuty analysis of whole and systematic life-long vocation
- Basic research on practical curricula for each vocation
- Relocation of research and research functions to Tottori prefecture and Survey research to improve the voca tionalability development system in the automobile field (Advanced Train ingDevelopment Office)
Development of training courses and materials
- Development of training materials
- Expansion of training curricula at each training school
Development of training methods and evaluation
- research on VET subjects for job seekers
- quality assurance for VET made according to "theAct of Job Seekers"
Information Channel
Provide information through HP, reports, special magazines, and the facilities for VETemployees.
In 2017, HP access number 2,034,135, downloads 79,679, research reports sent to 2,038 facilities.
Private co., public VET facilities, etc.
Change ofplans and actions of job training according to thechange of training needs and people
Applied Example
- Appl. to jobduty analysis and workers education as model data at companies and organization
- Appl. to revise standards of job training
- Appl. to teaching materials at public VET facilities
- Appl. To VET facilities for their curricula, syllabi, and practical subjects
- Appl. to training subjects to confirm states of technic and technology level of job seekers
- Appl. to job training conductedby prefectural branch office of JEED at private VET for their curricula and evaluation
7. Outline of the 4 years BachelorCourseof Science in Manufacturing Technology
The course of Sciencein Manufacturing Technology is an undergraduate course for 4 years.s"
It s education principle consists of Science-Technology –Skill, and aims to educate so-called "Process Innovator
who can work to operate, manage, and innovate at manufacturing sites, which involves quality, production and structural management.
At the same time, graduates will have enough knowledge to be VET instructors in future.
1. Features of Course
Setting combined practical/academic curricula (5,616 hours that is 1.8 times of study of normal colleges in Japan, and the contents of real exercises occupy 60 % of the total learning hours and the students can be real engineers and technologists. )
Real technic and technology can be acquired in small classes of skill exercise, experiment, and practice.
Bachelor of Science in Manufacturing Technology is given as well as many kinds of technology status.
2. Department, number, current number
| Department | quota class |
1yr * | 2yr * | 3yr * | 4yr * | total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mech. Eng. | 20 | 30 | 27 | 15 | 18 | 90 |
| Elec. Eng. | 20 | 28 | 24 | 24 | 16 | 92 |
| Electro-infoeng. | 20 | 26 | 36 | 19 | 29 | 110 |
| Architecteng. | 20 | 30 | 31 | 29 | 26 | 116 |
| total for year | 80 | 114 | 118 | 87 | 89 | 408 |
* Present numberofstudents
3. Place of employment after completion
| Department | JEED | Private corporation | Govemment organization and the other |
other Graduate school |
total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mech. Eng. | 10 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 18 |
| Elec. Eng. | 7 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 15 |
| Electro-info eng. | 14 | 13 | 1 | 0 | 28 |
| Architect eng. | 10 | 16 | 0 | 0 | 26 |
| total | 41 | 45 | 1 | 0 | 87 |
8. International collaboration
Upgrading ability of VET instructors in developing countries
outline
- invite VET instructors in developing countries to Japanfor 1 year
- upgrade ability of those by teaching training methods, career consulting, planning ability of VET
receiving country
- ASEAN countries as Cambodia, Indonesia, Malaysia etc.
receiving time
- April every year
(Thenumberofpeopletrainedso far)
【invited VET instructors】since1963
1642 persons from 92 countries
【government-financedoverseasstudents】since1992 to 2011
undergraduate course : 254 students from 8 countries.
graduate course : 21 students from 4 countries
9. Cooperation to World and National Skills Competitions and Youth Monodzukuri(manufacturing) Skills Competition, etc.
cooperating action
referees and competition members : subject preparation, management, cooperation on preparation
main cooperating sort of operation
mechanics : assembly, molding, precise machinery assembly, mechatronics, mechanical drawings, milling machine, mechanical CAD, electro discharge machining, metal press, structural ironing, plating, molding, etc.
Electric : shop electrics, electrics operation, assembly of electro machinery, maintenance, drawings, etc
Electro/info : assembly of electro machinery, assembly of electric circuit, info. technology, LSI manufacturing, print assembly, ITPC network support, info. Network support, etc.
Architecture : furniture, fittings, carpenter, blocking, tiling, wood machining, etc
2018 National Skills Competition (total 46 members of PTU joined)
techno chairman 1, oper. member 1, referee of competition 38, supporter 6
2018 Skill Grand Prix. (total 6 members)
techno chairman 1, oper. Member 1, referee of competition 4
2018 Youth MonodzukuriSkills Competition (total 30 members of PTU joined)
techno chairman 1, vice chairman 1, oper. member 1, competition member 18, supporter 9.
2017 World Skills Competition (3 Members of PTU joined)
technical delegate 1, skill competition Manager1,expert 1
